Contribution to CO2 emission reductions by energy efficient products and services in Japanese Electrical and Electronics industries
Source: “Contributing to Avoided Emissions through the Global Value Chain ― A new approach to climate change measures by private actors ―(November 2018),” Japan Business Federation
http://www.keidanren.or.jp/en/policy/vape/gvc2018.pdf
Summary
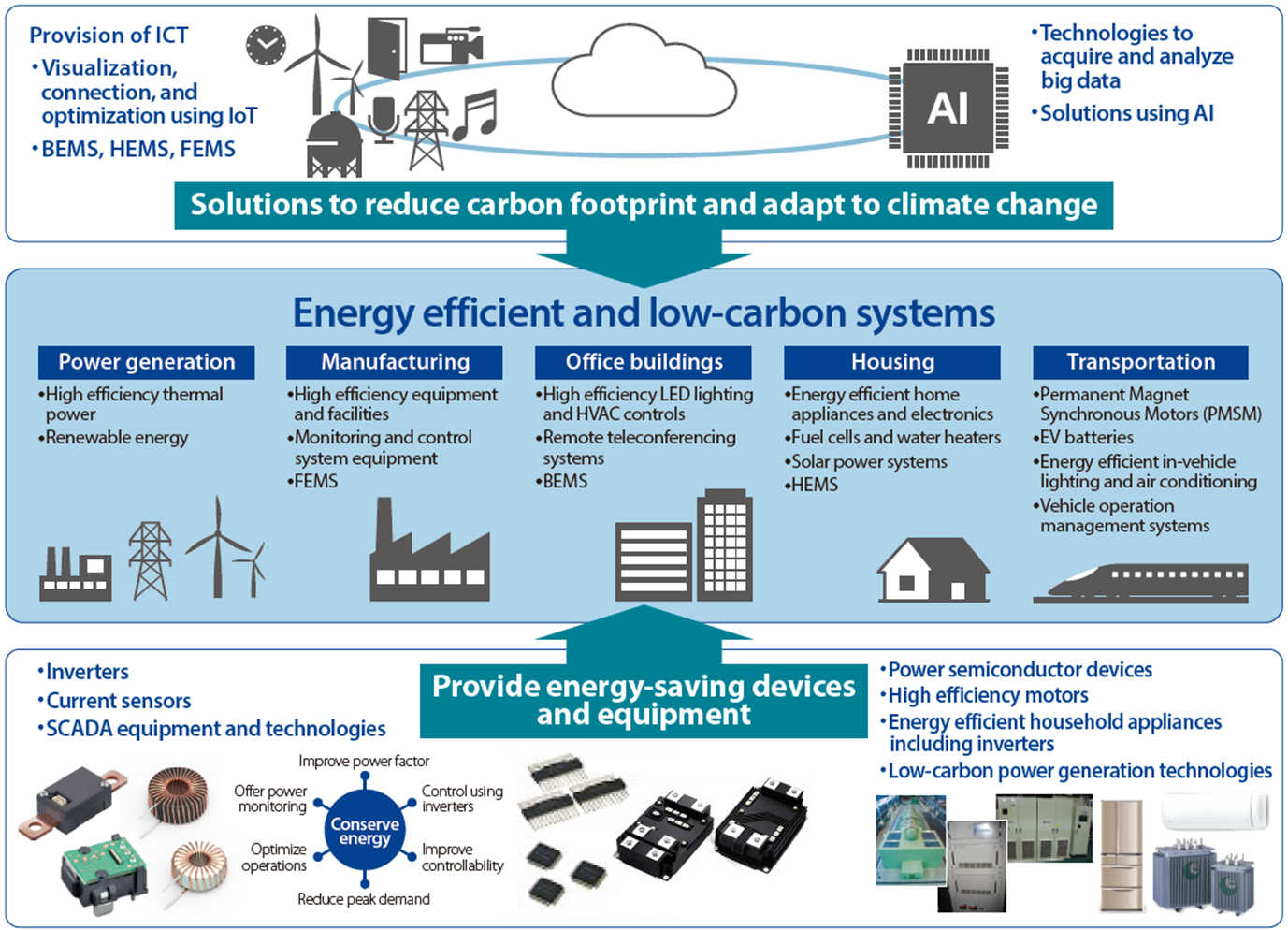
Electrical and electronics industries contribute to global warming prevention by providing technologies as well as products and services that achieve energy savings and decarbonization in cooperation with other actors in various sectors of society.
The Liaison Group of Japanese Electrical and Electronics Industries for Global Warming Prevention has formulated methodologies for calculating avoided CO2 emissions, and publishes assessment results (every fiscal year) under the Commitment to a Carbon Neutrality. (as of January 2022, methodologies have been formulated for 24 products and services/solutions, and components).
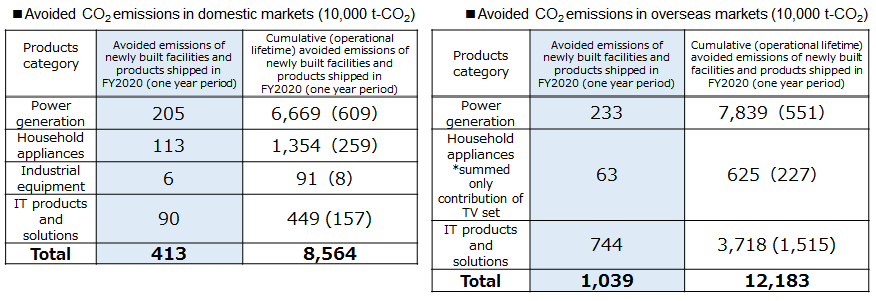
Quantification results of avoided emissions
 【Calculation of avoided emissions】
【Calculation of avoided emissions】
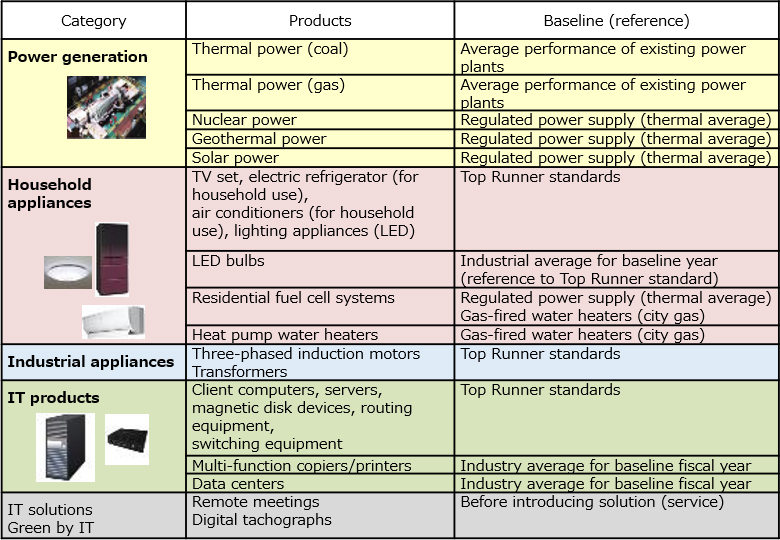
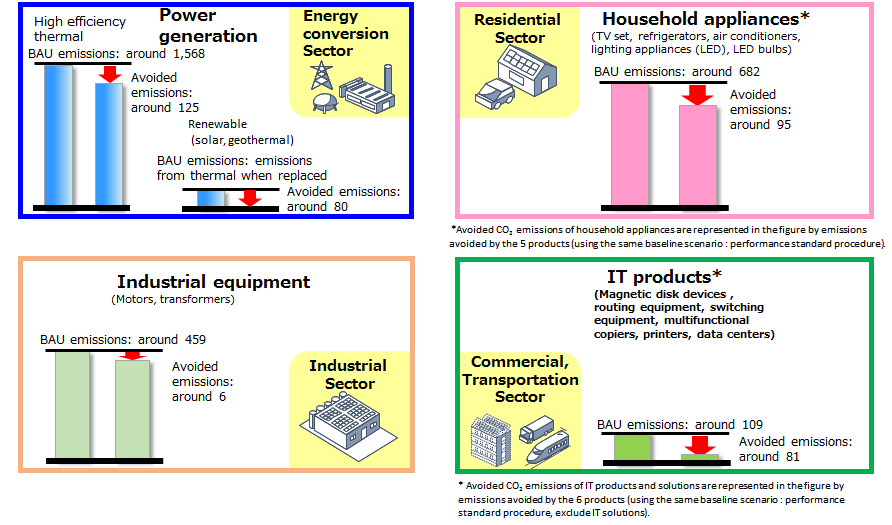
In accordance with the methodologies formulated by the Liaison Group of Japanese Electrical and Electronics Industries for Global Warming Prevention, efforts made by member companies participating in the Commitment to a Low Carbon Society Carbon Neutrality Action Plan were aggregated and assessed. The values in round brackets represent avoided emissions achieved by semiconductors and electronic components. Estimates were with consideration of the contribution ratio derived from the inter-industry table. Due to the rounding of values, totals may differ from the sum of categories.
(1)Baseline scenario and assumptions
Focusing on energy-intensive products and solutions that have become widely used but are expected by society to undergo continued efficiency improvements (technology development) (e.g. target products of the Top Runner program under the Law Concerning the Rational Use of Energy) under the Commitment to a Low Carbon Society, which is currently promoted by the Liaison Group of Japanese Electrical and Electronics Industries for Global Warming Prevention, the Liaison Group formulated methodologies for calculating avoided CO2 emissions, with a view to reducing energy consumption by users and consumers when a product is in use.
Avoided emissions of major products(ⅰ)
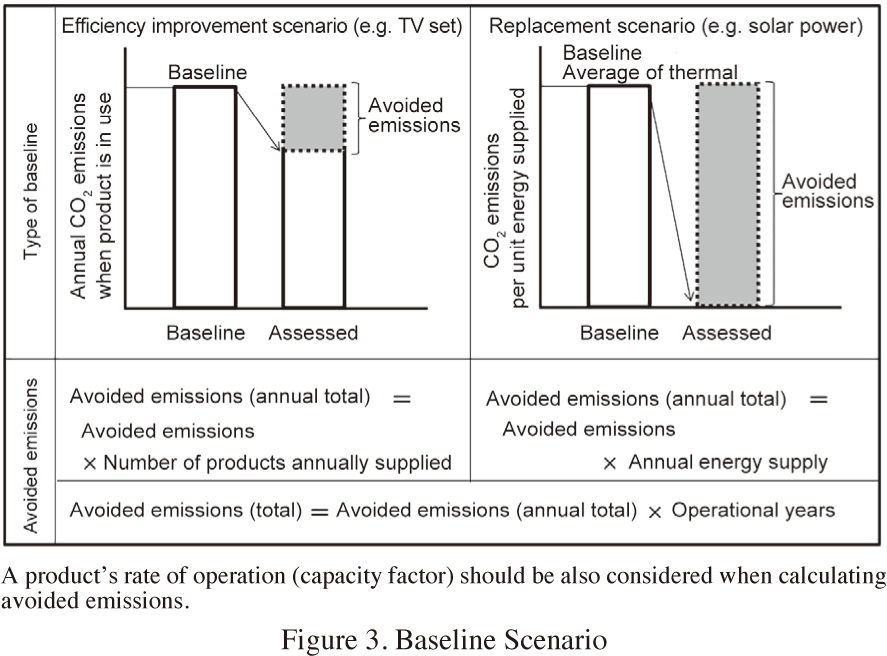
The baseline scenario is approached as follows:
Performance standard procedure
— Comparisons with standards stipulated in law and regulations or industry average.
Project specific procedure
— Comparisons with specific products or systems that are replaced with the assessed product.
- (ⅰ)
- The approach taken determining the baseline scenario follows “Determining the baseline scenario” in IEC TR 62726 (2014) Ed 1.0 Guidance on quantifying greenhouse gas emission reductions from the baseline for electrical and electronic products and systems. Individual methodologies are disclosed on the industry’s website for information associated with the Commitment to the Low Carbon Society.
http://www.denki-denshi.jp/implementation.php
The methodologies for calculating avoided emissions of other products, such as semiconductors, electronic components, and IT solutions (Green by IT) are provided below.
Avoided emissions of semiconductors and electronic components (electronic devices)(ⅱ)
Avoided emissions were calculated by estimating the contribution ratio of semiconductors and electronic components, using the cost to value ratio of value-added of components and finished products estimated based on the value of inter-industry transactions / value-added provided in the inter-industrial table (Input-Output Table).
- (ⅱ)
- In order to claim that avoided emissions constitute a part of the group of products covered by the Commitment to a Low Carbon Society, avoided emissions should be calculated in accordance with the guide to calculation methodologies issued by JEITA Semiconductor Board and Electronic Component Board. Calculation methodologies for components are disclosed on the industry’s website for information associated with the Commitment to the Low Carbon Society.
Avoided emissions through IT solutions (Green by IT)(ⅲ)
Social contributions using IT solutions are calculated by determining appropriate scenarios (derived from changes seen in scenario factors) that represent emissions before and after introducing the solution
- (ⅲ)
- JEITA Green IT Promotion Council has formulated methodologies for calculating avoided emissions, including determining baselines, and has made them available on their website:
https://home.jeita.or.jp/greenit-pc/contribution/index.html
(2)Scope of quantification
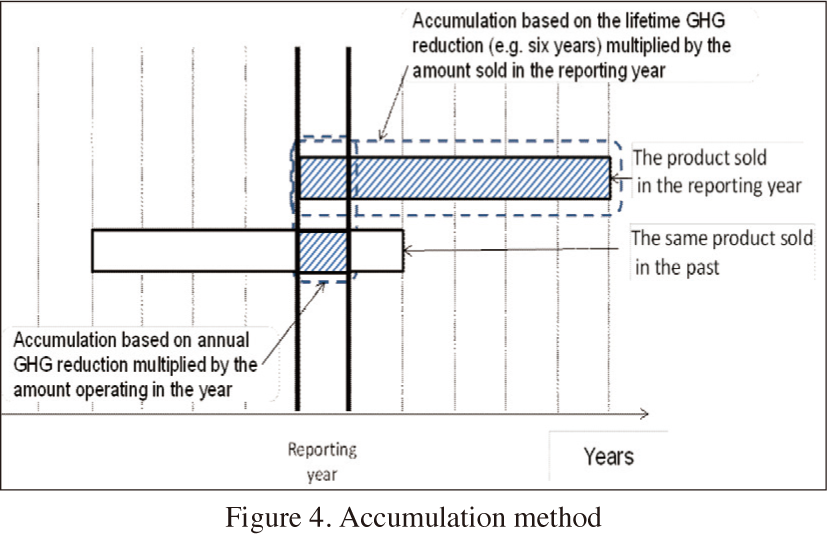
This case study covered avoided CO2 emissions at the product use stage and solution use stage, because electronic and electrical products being durable consumer goods, they emit the most CO2 when in use, which has also been proven true in assessments of life cycle CO2 emissions. Another reason is that users and customers can contribute to reductions when they use products. The concept of the “Accumulation Method”(ⅳ) is provided below:
Assessment year: “products’ annual GHG emissions reduction”
Under the Commitment to a Low Carbon Society, assessment are performed for on year in the annual follow-up.
Operational years: “Products’ lifetime GHG emission reduction”
The length of product lifetimes is determined separately for each assessed product, in accordance with law and systems, legal service life of major models, and industry averages.
- (ⅳ)
- Based on IEC TR 62726 (2014) Ed 1.0 Guidance on quantifying greenhouse gas emission reductions from the baseline for electrical and electronic products and systems, 6.10.3 Accumulation method