1
Our Recognition of Urgent Challenges
in View of Global Warming

World Trends Surrounding Global Warming
The movement toward carbon neutrality has grown in earnest in Europe since around 2019. The United States is rejoining international efforts against climate change with ambitious targets along with the change of administration in 2021, and many developing countries have also set carbon-neutral targets.
In October 2020, Japan declared the realization of carbon neutrality by 2050. This declaration is specified as the basic principle in the revised "Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming (enforced in April 2022)." The government set a 2030 GHG reduction target as well in line with this level of carbon neutrality, and specific measures are currently under way in earnest to develop Green Growth.
In accordance with these domestic and international trends, industries and com- panies in Japan are working to prevent global warming on a society-wide as well as a global level in cooperation with various sectors.
Missions of Electrical and Electronics (EE) Industries
Providing a wide range of products and services to all sectors
Japanese EE industries supply a variety of products and services (appliances, devices, solutions, etc.) to many sectors, including industrial, business, household, transportation and energy conversion sectors. With such characteristics in mind, we aim to contribute to the prevention of global warming, while having our sights set on the entire value chain.
Contribution throughout the value chain
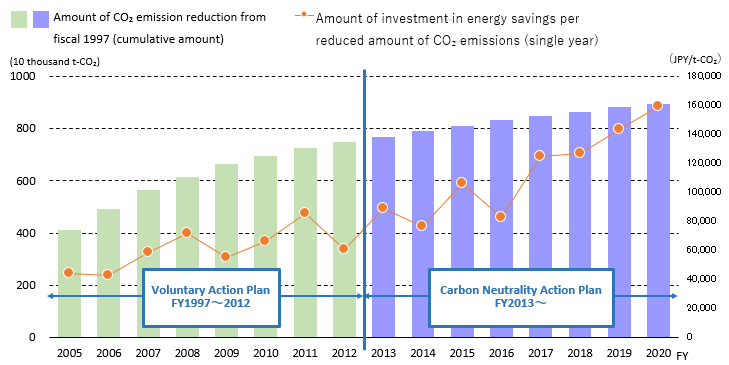
Japanese EE industries have continued to implement energy-saving measures in the production stage and have strived to manufacture products in an energy-ef- cient manner while showing an increasing trend in investment amount per CO2 reduction amount.(Fig. 1)
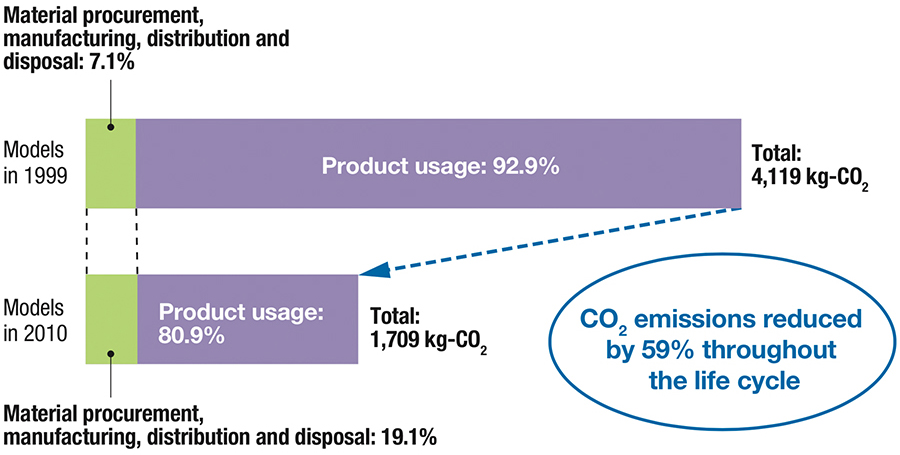
On the other hand, comparison of CO2 emissions at each stage in the life cycle of products shows that some products such as household appliances and industrial equipment, in particular, tend to generate more CO2 emissions in a product usage than production stage.(Fig. 2)
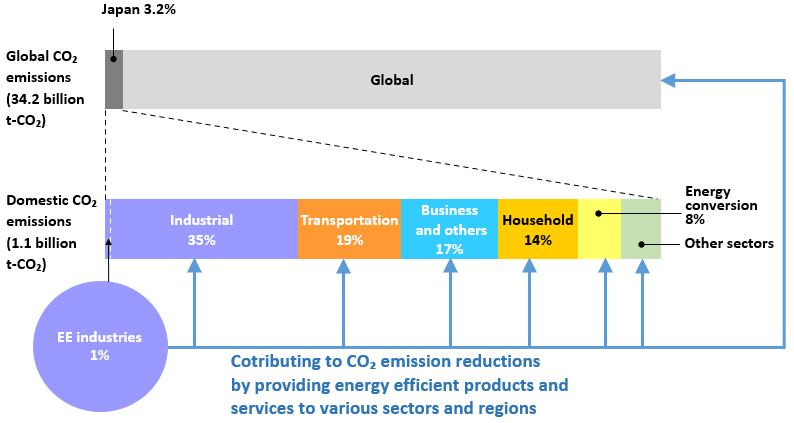
Therefore, we will contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions in the entire value chain by improving the energy ef ciency of appliances and devices, advancing the development of IT/IoT solutions enabling more ef cient energy usage, and spread- ing these improvements and development throughout society.(Fig. 3)
Fig. 1 Results of amount of investment in energy savings and cumulative
energy savings(CO2 emission reduction)
Fig. 2 Comparison of CO2 emissions in a life cycle (e.g. refrigerators)
Source:The Japan Electrical Manufacturers’ Association
Fig. 3 Sectorial analysis of CO2 emissions (FY2019) and contribution by EE
industries to sectors
Source:Created by Liaison Group of Japanese Electrical and Electronics Industries for Global Warming Prevention based on "Total CO2 emissions - World" by IEA Data Services, "Japan's Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data in FY2019 (Final Figures)" by Greenhouse Gas Inventory Of fice of Japan, National Institute for Environmental Studies, and "Commitment to a Low Carbon Society FY 2020 Follow-up Results (Performance in FY2019)" by Keidanren (Japan Business Federation)
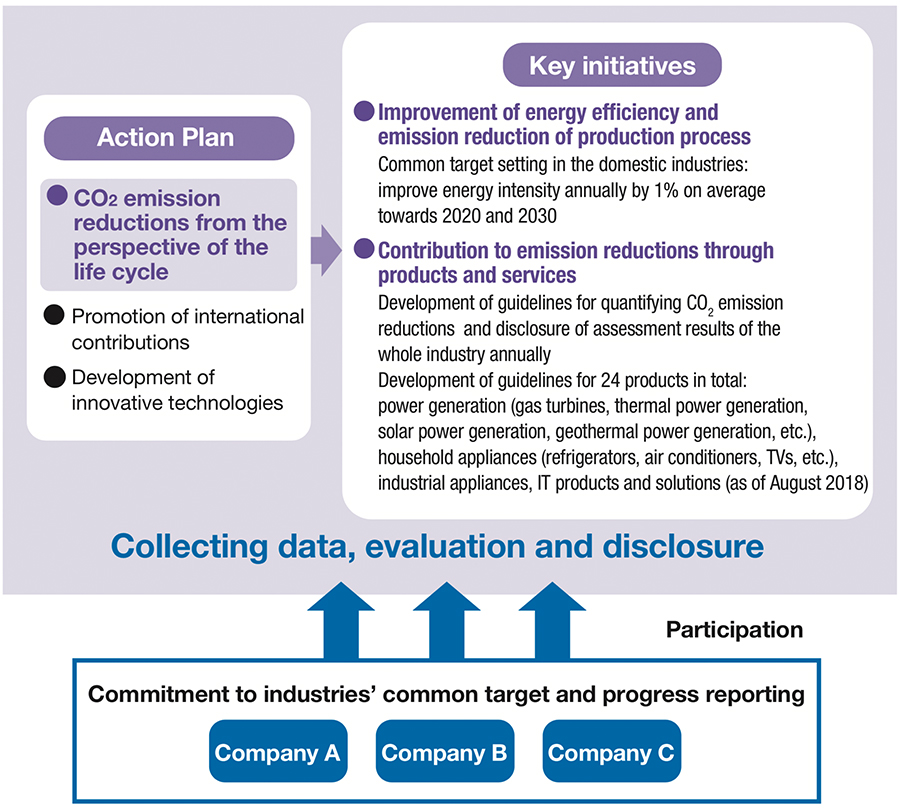
Electrical and Electronics Industries’ “Carbon Neutrality Action Plan”
(Reduction of Energy-oriented CO2 Emissions)
Japanese EE industries have participated in The Carbon Neutrality Action Plan※1 formulated by the Keidanren, and are aiming to improve the energy efficiency of production processes by an average of 1% annually.
Also, for the purpose of contributing to CO2 emission reductions in society through products and services, we have developed guidelines for quantifying CO2 emission reductions and disclose the results of the whole industry annually.
Furthermore, in Phase II of the Action Plan, we have added a new challenge target to reduce CO2 emissions by about 46% by 2030 compared to 2013, aiming to play a part in achieving Japan’s medium-term goal. We will take further actions to carry out these goals. (Figs.4-7)
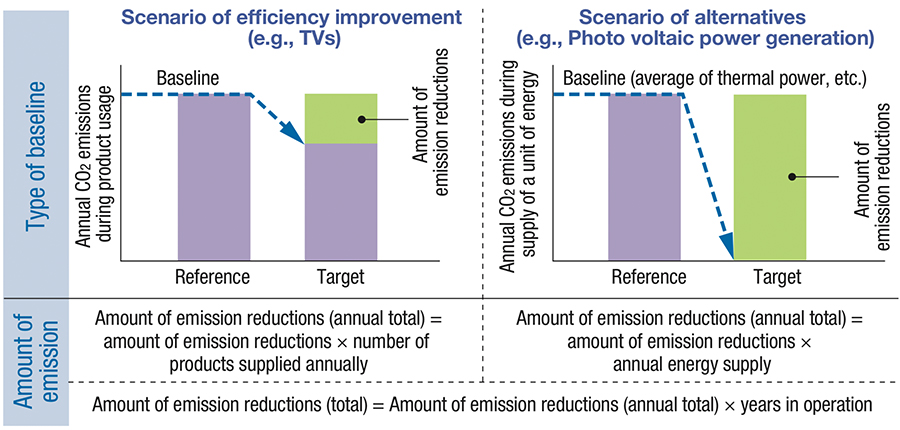
We also support and participate in industry initiatives for quantifying contribution to avoided emissions, through the global value chain promoted by the Japanese government.
- ※1
-
In December 2009, the Keidanren declared a "Commitment to a Low Carbon Society," as a shared vision of the Japanese business community harnessing its technological prowess, and assumed an instrumental role in the drive to halve global greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2050.
As the world's concerns and expectations become increasingly focused on achieving carbon neutrality, in November 2021, the Keidanren has set out the new "Carbon Neutrality Action Plan," with a private sector vision for carbon neutrality by 2050, which it strongly promotes (1) Developing and introducing visions and innovative technologies toward carbon neutrality by 2050, (2) Reducing emissions from domestic business operations, and (3) Strengthening co-operation with other interested groups and promoting contributions at the international level.- ・KEIDANREN's Commitment to a Low Carbon Society(December 2009)
http://www.keidanren.or.jp/english/policy/2009/107.html - ・Phase II of the Commitment to a Low Carbon Society(April 2015 )
http://www.keidanren.or.jp/policy/2015/031.html (Japanese text only) - ・Urgent Policy Proposal toward Achieving Green Growth(June 2021)
http://www.keidanren.or.jp/en/policy/2021/057.html - ・Keidanren Carbon Neutrality Action Plan(November 2021)
http://www.keidanren.or.jp/policy/2021/102.html (Japanese text only)
- ・KEIDANREN's Commitment to a Low Carbon Society(December 2009)
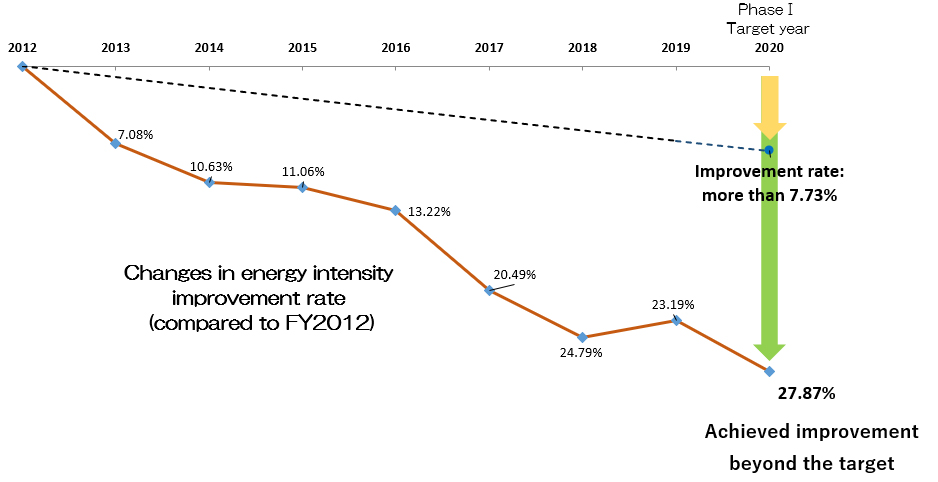
Fig. 5:PhaseⅠ Improvement Result of energy efficiency in production processes
By continuing energy-saving efforts without slack, we achieved an improvement of 27.87%, exceeding the energy intensity improvement of 7.73% (compared to FY2012) set as the target for FY2020
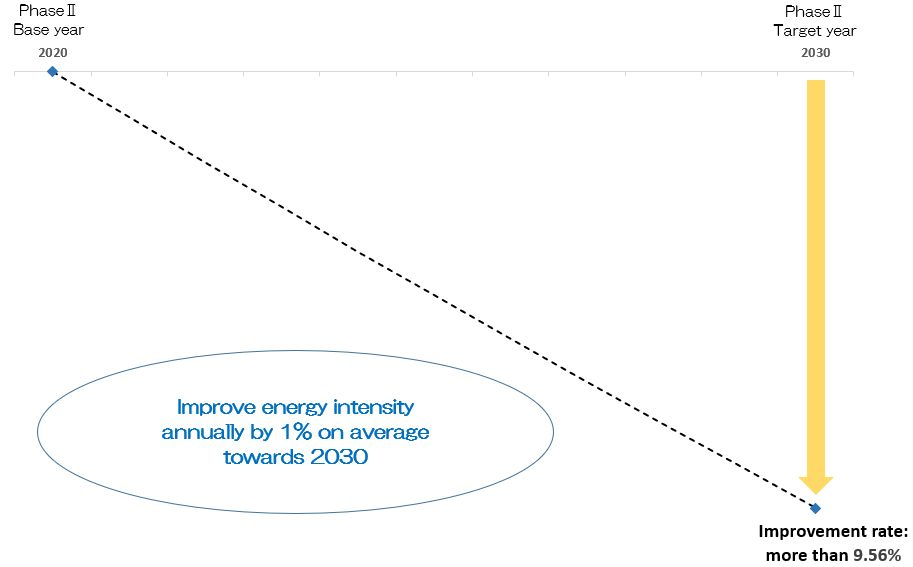
Fig. 6:PhaseⅡ Commitment target to improve energy efficiency of production process
Based on the improvement by 2020, the Phase II target was reviewed in September 2021.
With FY2020 as the base year, the target is to continue the average annual improvement rate of energy intensity of 1%.
Initiatives for the Reduction of Greenhouse Gases Other than Energy-oriented CO2
Japanese EE industries are working on the reduction of not only energy-oriented CO2 but also other various greenhouse gases.
For example, greenhouse gases (HFC, PFC, SF6, NF3, etc.) are used in the manufacturing process of semiconductors and liquid crystal displays, for cleaning agents and solvents※2 of electronic components, and for electrically insulating gases for power equipment. We have set voluntary emission reduction targets for each product area and are aiming to achieve them.
- ※2
- Due to being volatile, cleaning agents and solvents are included in greenhouse gases.